Objects and Records
This page explains the most important concept in AnyDB: objects.
Everything else builds on this.
What is an object?
Your business contains many real things.
We call them Objects in AnyDB.

An object in AnyDB represents a real business entity.
Examples include:
- customer
- vendor
- project
- order
- asset
- warehouse
- inspection
What an object contains

Each object can include:
- structured fields such as dates, numbers, and status
- files and documents
- comments and activity history
- attached child objects
- links to other objects
You open one object and see everything related to it.
Object can also contain other objects.

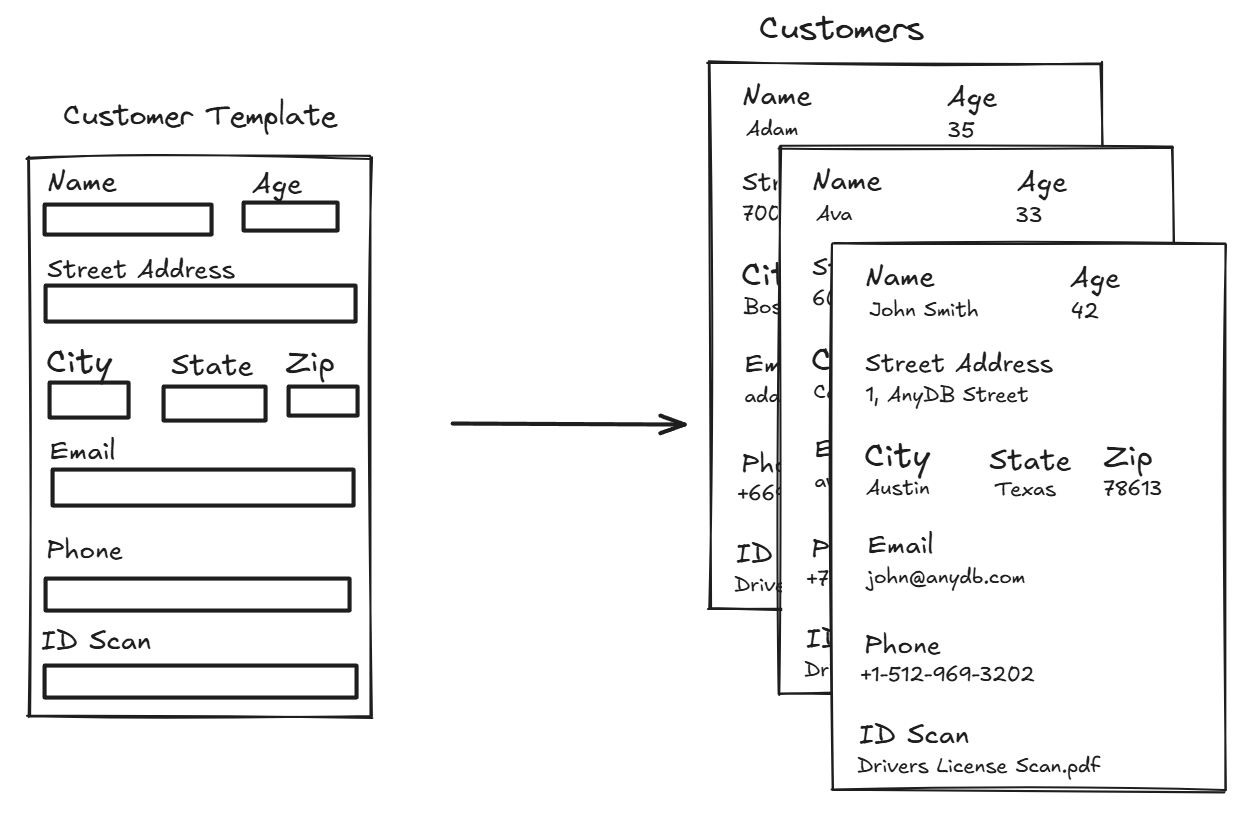
Records and templates
A record is a single instance of an object. Say you have an object type called "Customer". Records are customers you create for example "Acme Corp" and "Globex Inc".
A template defines the structure for records of the same type.
For example:
- Customer is a template
- Each customer profile you create is a record of that template
Templates help you:
- keep data consistent
- scale without redesigning structure
- evolve layouts over time
For example, if you need to create a new customer profile, select the Customer Profile template. This will automatically generate a repeatable structured business record for filling customers.
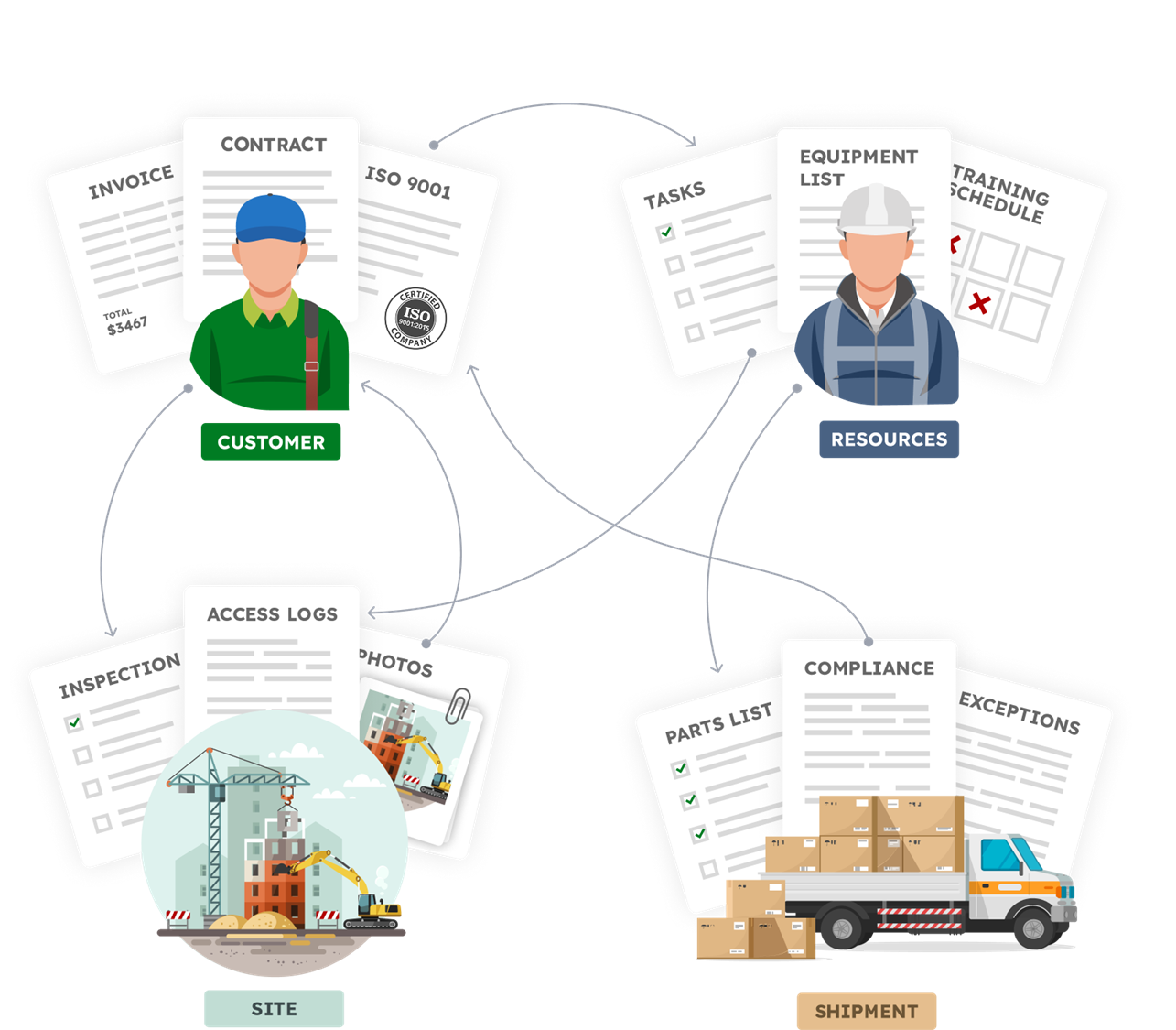
Objects can exist independently
Some objects make sense on their own and they can be considered as top level objects.
- customers
- vendors
- products
- employees

Other objects only make sense as part of something else and should be attached to a parent object.
- order lines
- budget line items
- invoice line items
- inspections
- tasks
- checklists