Teams & Databases
Understanding how Teams and Databases work together is key to using AnyDB effectively.
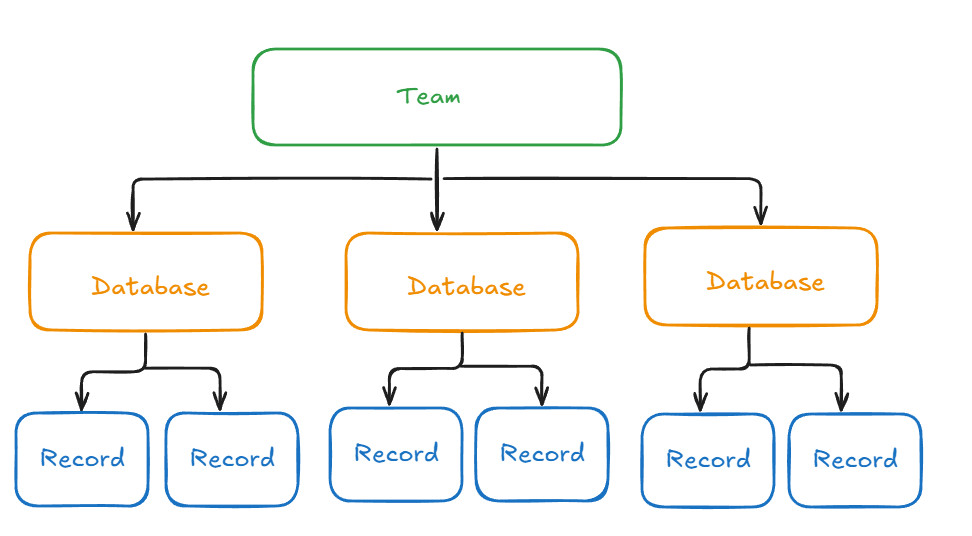
Teams in AnyDB
A Team is your top-level workspace in AnyDB. Teams bring people together to manage Databases, share records, and collaborate on workflows.
Key Concepts
-
Multiple Databases per Team
Each team can include unlimited number of databases, organized by department, function, or project. -
Invite & Manage Members
Add users to your team and assign roles that determine what they can access or edit. -
Groups for Simpler Permissions
Create groups to manage permissions across multiple users more efficiently.noteBilling is tied to Teams.
Each team is treated as a separate billing unit. If you're on a paid plan, adding multiple teams may result in multiple subscriptions.tipBest Practice:
For most organizations, especially small to mid-sized teams, we recommend using a single team with multiple databases. This keeps billing simple, centralizes permissions, and improves visibility across functions.
Example Team Structures
-
Company-Wide Team – Ideal for small businesses sharing all databases in one place
-
Department Teams – Separate teams for HR, Sales, Finance, etc., each with their own databases and members
-
Project Teams – Temporary workspaces focused on a specific initiative or client
cautionConsider billing before creating multiple teams.
While multiple teams are supported, each team has its own billing and user limits. If you're unsure, start with one team and scale your databases within it.
Databases in AnyDB
In AnyDB, your structured business data is stored as records—individual records like a customer, an invoice, or a project task. These records live inside Databases, which group related records together for easier access, tracking, and control.
Key Concepts
-
Record Collections
Databases organize related records—for example, customer records, job applications, or inventory items. While a database can contain identical records, they don't have to. You can mix and match any kind of records inside a Database. -
Permission-Based Access
Control who can view, edit, or manage records within each database by assigning roles to members or groups. -
Reusable Templates
Use templates to standardize how records are created and ensure consistency across your team.
Example Databases
- Sales Database – Includes records for leads, deals, and customer interactions
- HR Database – Contains employee records, onboarding documents, and review forms
- Finance Database – Stores invoices, budgets, and expense reports
- Project Management Database – Tracks tasks, milestones, and team assignments
How Teams and Databases Work Together
Here’s how Teams and Databases connect inside AnyDB:
- Create a Team – Set up a workspace for your company, department, or project
- Add Databases – Group related records into databases within the team
- Invite Members – Add teammates and assign them appropriate roles. See User Management for details.
- Manage Permissions – Define who can access or modify each database and its records
Example
At Acme Corp, you might organize AnyDB like this:
- A single team that contains databases for Sales, HR, and Finance
or - Separate teams for each department, each managing its own databases and records
Both approaches are valid, but billing and user management are simpler with fewer teams.