When a company grows, one of the biggest challenges is maintaining efficiency without compromising quality and reliability in the delivery of products or services. With operations management, you gain the guidance needed to transform resources (such as people, materials, capital, and data) into valuable results.
Don’t mistake the concept for pure theory: operations management offers practical frameworks, performance indicators (KPIs), and methodologies that help expanding teams organize processes, reduce waste, and make informed decisions.
For founders, operations managers, and PMO leaders, mastering its fundamentals is a key step to sustaining growth with consistency. Check it out!
What Is Meant by Operations Management?
Operations management is the discipline that structures and controls processes that convert inputs, such as people, technology, equipment, capital, and information, into goods and services.
In short, it’s about creating value.
And what does that mean? Transforming resources into results in a way that enables the company to serve customers predictably and at scale. It involves balancing costs, timelines, and quality standards, while ensuring the organization stays flexible to adapt to market changes.
The main domains that make up operations management include:
- Process design and planning: defining how the work will be done.
- Scheduling: organizing deadlines and activity sequences.
- Inventory management: optimizing materials and stock control.
- Capacity planning: ensuring resources can meet demand.
- Quality management: guaranteeing consistent and reliable products and services.
- Supply chain management: coordinating suppliers, logistics, and deliveries.
- Continuous improvement: reviewing and refining processes regularly.
Core Functions & Frameworks
Operations management relies on essential functions and proven frameworks that help companies structure processes and drive efficiency.
And, for your business to stop “firefighting” and start operating with predictability, let’s explore the 7 core functions of operations management, the 5 Ps that explain its pillars, the 4 most common types of operations, and the market’s most widely used methodologies.
The 7 main functions of operations management
- Forecasting & demand planning: estimating future demand for products or services to align production and capacity.
- Capacity planning: assessing whether available resources (people, machines, technology) are sufficient to meet demand.
- Process design: structuring how activities will be carried out, ensuring efficiency and standardization.
- Scheduling: defining the order, deadlines, and responsibilities for task execution.
- Inventory/warehousing: managing stock levels to avoid both excesses and shortages.
- Quality management: ensuring that products and services meet performance standards and customer satisfaction.
- Continuous improvement: regularly reviewing and enhancing processes, reducing waste, and increasing productivity.
The 5 P’s of operations management
- People: employees involved; example: training customer service teams to improve response time.
- Processes: organized steps to deliver value; example: implementing a digital order approval flow.
- Products/Services: what the company delivers; example: a clinic offering both in-person consultations and telemedicine.
- Plants/Places: where processes take place; example: logistics warehouses located near strategic clients.
- Planning & Control: monitoring and adjusting execution; example: weekly performance meetings with key indicators
The 4 types of operations
- Project: unique, long-term activities; e.g.: implementing new software in a company.
- Jobbing: made-to-order production; e.g.: graphic design or consulting services.
- Batch: production in groups; e.g.: bakeries baking bread in batches or restaurants preparing meals for events.
- Mass/Continuous: standardized, large-scale production; e.g.: call centers or SaaS support operating 24/7.
Supporting frameworks and methodologies
In addition to functions and classifications, operations management relies on frameworks that help improve performance and reduce inefficiencies, such as:
- Lean to eliminate waste and focus on customer value.
- Six Sigma to reduce variations and defects.
- Theory of Constraints (TOC) to identify and resolve bottlenecks in the flow.
- S&OP (Sales & Operations Planning) to integrate sales and operations in planning.
- MRP/ERP (Material Requirements Planning / Enterprise Resource Planning), systems to manage resources and integrate data.
- SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures) with standardized instructions that ensure consistency in work.
Operations Management Strategies for Growing Teams
The secret to preventing the complexity of your team’s growth from becoming an obstacle is this: replace constant reaction to problems with routines that create flow and predictability.
Below are tactical practices that can be applied simply but deliver significant impact when put into action.
Capacity & Workload Shaping
- Why it matters: prevents overload during demand peaks and improves resource utilization.
- How to start this week: test demand smoothing, adopt flexible shifts, promote cross-training, and calculate takt time to balance production pace with demand.
Process Mapping & Standard Work
- Why it matters: reduces variation and errors by standardizing tasks.
- How to start this week: draw a simple value stream map, create one-page SOPs for critical routines, and apply error-proofing techniques (poka-yoke).
Quality at the Source
- Why it matters: avoids rework and extra costs, ensuring consistent deliveries.
- How to start this week: use visual checklists, work in smaller batches, adopt the “first-time-right” principle, and implement visual controls to prevent errors.
Inventory & Lead Time Control
- Why it matters: poorly managed inventory ties up capital or creates stockouts.
- How to start this week: define reorder points, adopt safety stock, classify items with the ABC/XYZ matrix, and apply Little’s Law to reduce queues and waiting time.
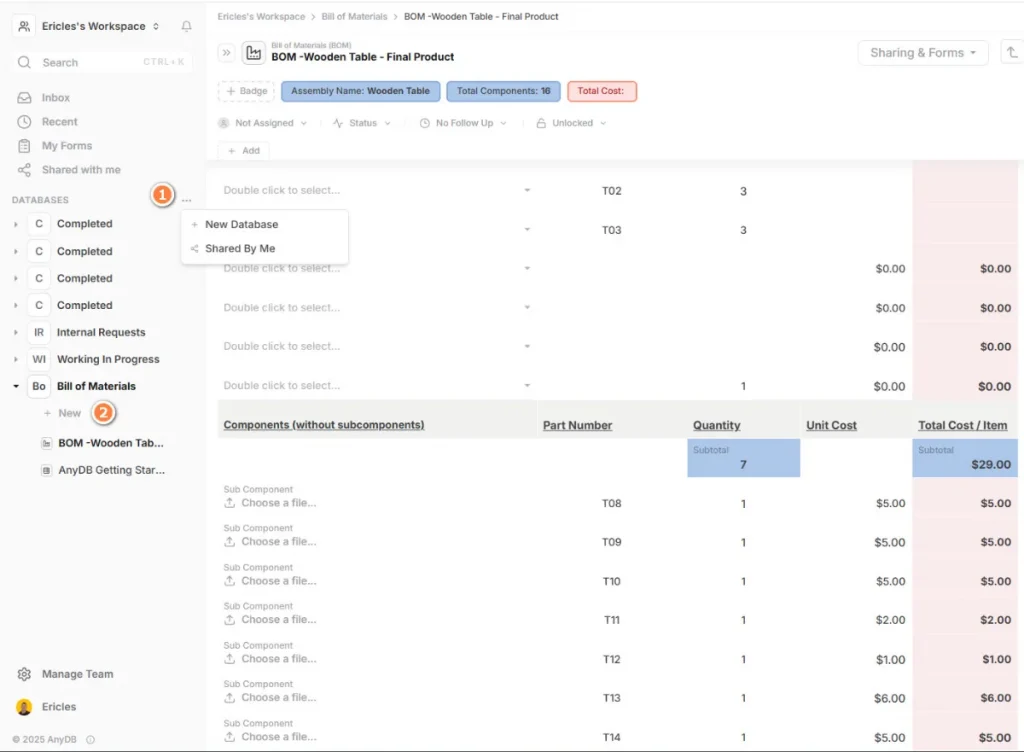
Explore the Bill Of Materials Template on AnyDB and streamline your production planning. See how smart cost calculations and component tracking help you decide what to make or outsource!
Operating Cadence
- Why it matters: creates discipline for follow-up and strategic alignment.
- How to start this week: implement daily standups, weekly ops reviews, and monthly S&OP cycles; align everything with OKRs to connect execution and strategy.
Systems & Data
- Why it matters: ensures a single source of truth, avoiding information loss in scattered spreadsheets.
- How to start this week: centralize tasks, forms, vendor/customer data, SLAs, and dashboards in an operations management system accessible to the team.
KPIs That Matter (Formulas & Targets by Function)
Measuring performance is what turns operations management into tangible results. Tracking the right KPIs helps growing teams identify bottlenecks and align priorities.
Flow and Productivity
Key indicators such as Cycle Time (time to complete an activity), Lead Time (time between order and delivery), and OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness = Availability × Performance × Quality).
Service Performance
Focus on customer experience. KPIs like SLA Attainment % (tasks completed within agreed deadlines), First-Contact Resolution % (issues resolved on first contact), and CSAT/NPS (customer satisfaction and loyalty) show if value is being delivered consistently.
Reliability and Quality
Metrics such as Defect Rate (defects per unit), First-Pass Yield % (right-first-time deliveries), and Rework % (rework proportion), reveal whether processes operate efficiently. In logistics and production, metrics like OTIF % (On-Time, In-Full) and Schedule Adherence % are crucial to meet commitments and avoid delays.
Other KPIs complete the strategic view:
- Inventory: Inventory Turnover and Days Inventory Outstanding, indicating whether capital is well allocated. Explore how AnyDB supports this on our Inventory Management use case page!
- Productivity & Cost: Labor Utilization %, Cost per Output, and Capacity Utilization %, showing resource efficiency.
- Continuous Improvement: Kaizen actions closed, SOP adoption %, and Automation, reflecting progress toward more agile and sustainable processes.
To make sense of all these numbers, smart dashboards should combine leading indicators (like WIP and takt variance) with lagging indicators (like OTIF and costs), always using clear, consistent definitions.
If you want to simplify this journey, a system like AnyDB can help: centralizing operational records, connecting vendor and customer data, applying SOPs, and maintaining real-time dashboards, without ERP-level complexity.
Try AnyDB for free and take your operations management to the next level!
FAQs: Operations Management Basics
Learn more about operations management with the answers to the questions below:
It is the discipline that transforms resources (people, materials, capital, and data) into goods and services efficiently, with quality and reliability, delivering value to customers and sustainability to the business.
Forecasting & demand planning, capacity planning, process design, scheduling, inventory management, quality management, and continuous improvement.
People, Processes, Products/Services, Plants/Places, and Planning & Control, each serving as a pillar of operational execution.
Project (unique activities), Jobbing (made-to-order), Batch (production in groups), and Mass/Continuous (large-scale or continuous production), applicable to industries and services like SaaS, restaurants, and clinics.
What is AnyDB?
AnyDB is a unified, customizable data store designed to streamline and empower your entire organization. Effortlessly store, organize, and share custom business data to drive both internal and external operations across teams. Think of it as spreadsheets on steroids.Perfect for Sales, Marketing, Operations, HR, and beyond. Discover AnyDB





