Inventory Management with AnyDB
Overview
This guide shows how to use AnyDB to track and manage inventory across products, warehouses, and transactions. You’ll learn how to define warehouse locations, organize item-level records, and log stock movements—all from a flexible, spreadsheet-native workspace.
Business Problem
Most inventory tracking is done in disconnected spreadsheets or rigid systems that are hard to adapt. This results in inaccurate stock levels, poor visibility across locations, and manual effort to calculate costs and sales—leading to stockouts, overstocking, and lost margin.
Solution Summary
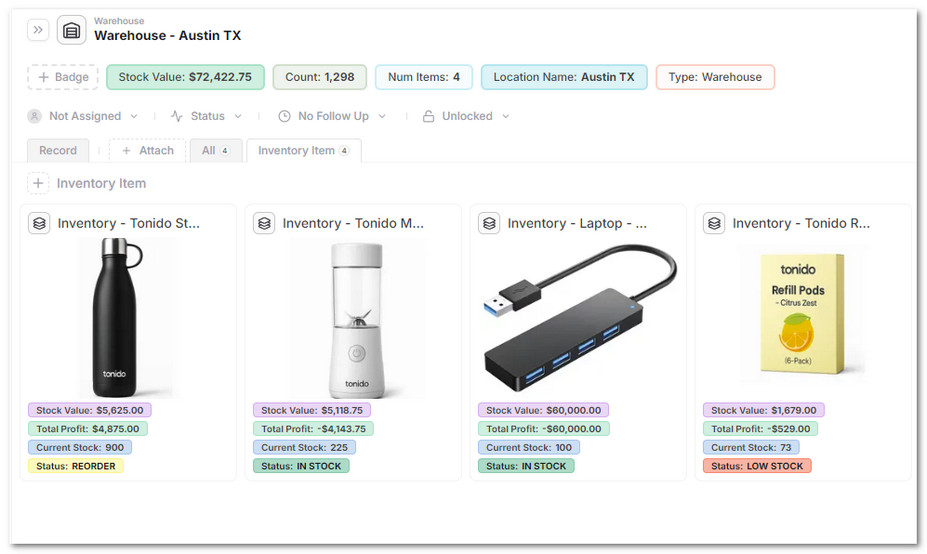
With AnyDB, you can:
- Store structured records for inventory items with stock, cost, and supplier data
- Set up warehouse locations and assign inventory to each
- Record every stock movement with type, quantity, and location
- Automatically calculate current stock, inventory value, and profit per item
- View dashboards and filter items by warehouse, status, or category
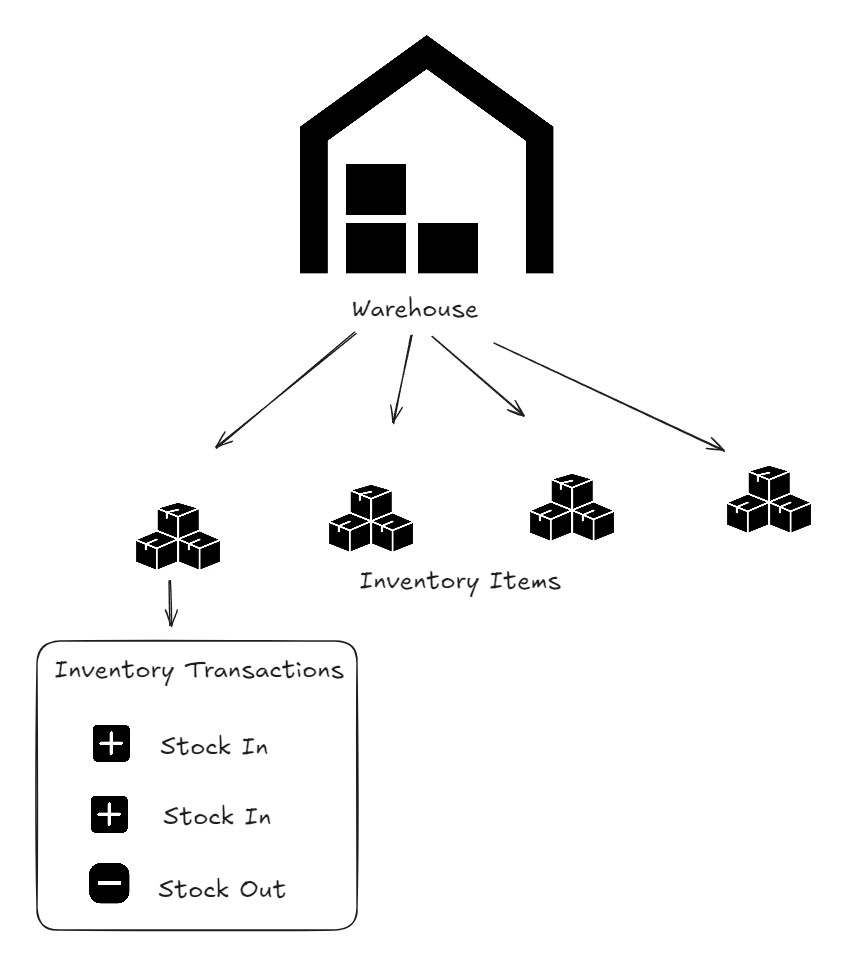
Step-by-Step Instructions
1. Create or Open an Inventory Database
- From the home screen, click + New Database
- Optionally, start with the ready to use Inventory Management solution, or start from scratch
- Name the database (e.g., “Main Inventory”, “Q3 Stock Tracker”)
- This database will hold all your templates: Warehouse, Inventory Item, and Inventory Transactions
2. Create a Warehouse
- Click + New Record to add a warehouse
- Select the Warehouse Record
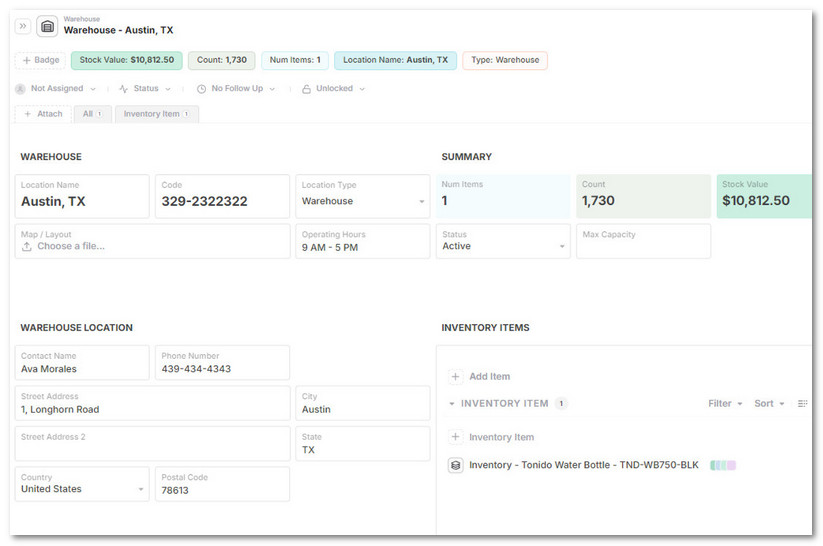
- Fill out fields like:
Location Name(e.g., Austin DC)Code(e.g., WH-AUS-01)Location Type,Address,Contact Info
- Attach a Map/Layout or capacity documentation
- Warehouse records will auto-calculate:
Item CountTotal Stock Value
3. Add Inventory Items to a Warehouse
-
In the Warehouse record, click Attach -> New Record
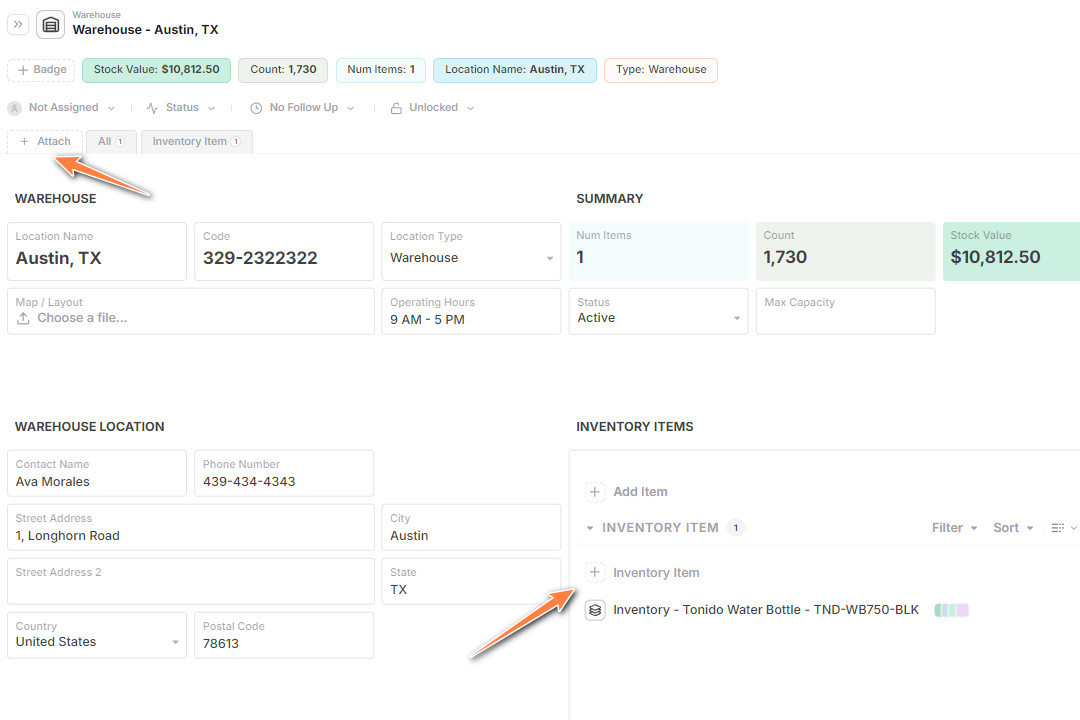
-
Select the Inventory Item Record
- You can choose to fill an initial starting quanity if you want to start without any transactions
-
Fill out core fields like:
Item Name,SKU,Unit of Measure,CategoryMin Stock LevelandReorder Levelfor alertsSupplierandImage
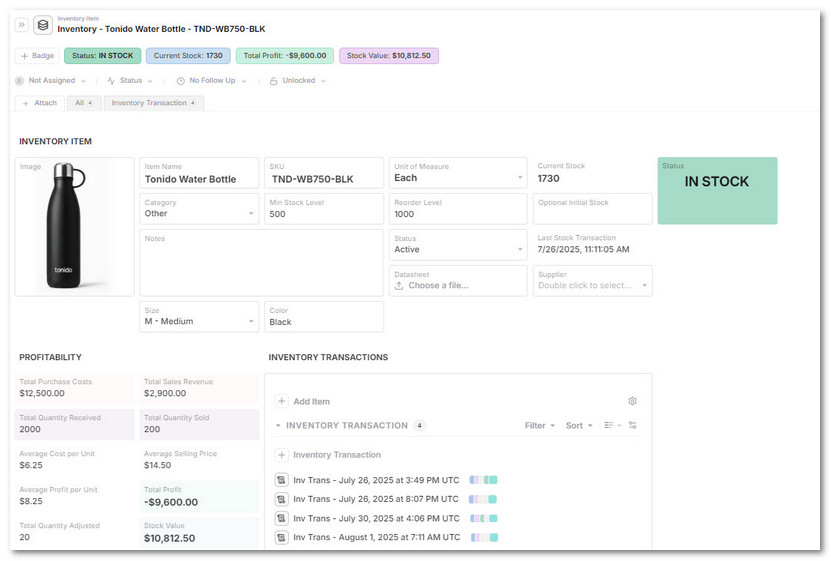
-
Auto-calculated fields will show:
Current Stockacross all transactionsStock ValueandTotal Profit
4. Log Stock Inventory Transactions for Each Inventory Item
-
In the Inventory Item record, click Attach -> New Record
-
Select the Inventory Transaction to track a stock movement
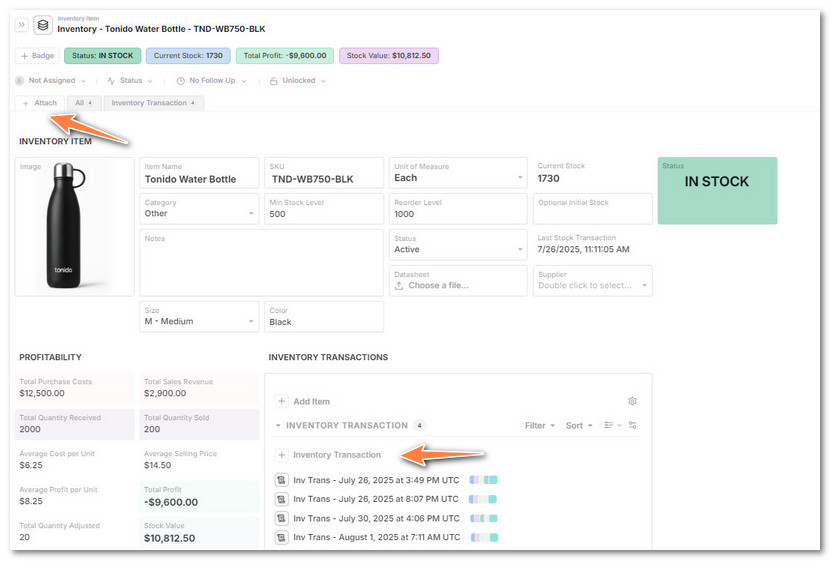
-
Choose a
Transaction Type:Stock In,Stock Out,Transfer, orAdjustment
-
Fill out:
Date,Quantity, and optionallyUnit CostorUnit Price- (Optionally) Link to the associated Inventory Item
- (Optionally) You can also attach:
Purchase Order,Shipping Docs,Inspection Notes
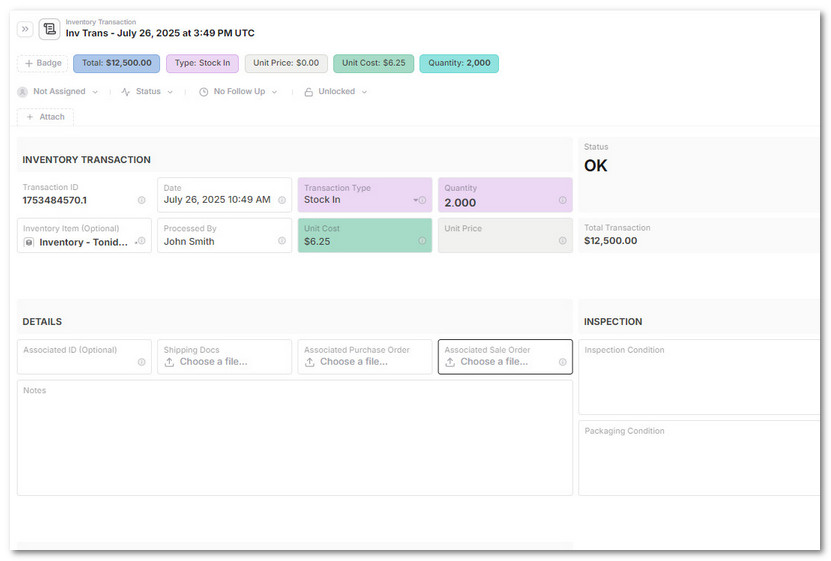
-
Formulas in the Inventory Item will auto-update:
- Stock levels
- Average cost / price
- Total revenue and profit
Data Model & Structure
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Item Name | Product or SKU name |
| SKU | Unique identifier |
| Unit of Measure | Each, Box, Kg, etc. |
| Category | Type or group (Electronics, Supplies, etc.) |
| Current Stock | Live calculated from transactions |
| Min Stock Level | Triggers LOW STOCK status |
| Reorder Level | Triggers REORDER warning |
| Warehouse | Linked location(s) |
| Supplier | Vendor contact |
| Stock Value | Inventory value (cost × quantity) |
| Total Profit | Sales – Purchase Costs |
| Linked Transactions | History of all stock activity |
| Attachments | Images, datasheets, POs, invoices |
Reporting & Views
Use saved views and dashboards to monitor:
- Low stock or below-reorder items
- Stock by warehouse or category
- Profitability by item or supplier
- Aging inventory or turnover
- Stock movement over time
Sharing & Collaboration
- Assign ownership to inventory managers or warehouse staff
- Share filtered views for audits, finance, or vendors
- Control access to item, transaction, or warehouse records
- Add inspection or packaging notes for compliance tracking
Tips & Best Practices
- Use dropdowns for consistent categories and transaction types
- Set up formula fields to flag reorder needs
- Organize warehouses by geography or fulfillment type
- Attach supporting documents for compliance and traceability
- Create templates to replicate item structure across SKUs
Pro Tip: Start with your physical warehouses, then add inventory items, then log stock movement to maintain clean, linked records.
Who This is For
- Operations Managers – track inventory across facilities
- Warehouse Staff – manage receiving, transfers, and audits
- Finance Teams – monitor cost, value, and margin
- Procurement Teams – drive replenishment decisions
- Auditors & Compliance – verify history and documentation
Why Use AnyDB for Inventory Management
| Benefit | How AnyDB Supports It |
|---|---|
| Real-Time Visibility | Stock and value auto-calculated from transactions |
| Linked Structure | Connect warehouses, items, and transactions seamlessly |
| Profitability Tracking | View cost, revenue, and margin per item |
| Flexible Record Layout | Add formulas, files, and child records to any item |
| Shareable Workspaces | Collaborate with internal and external teams |
| Scalable Templates | Reuse for hundreds of SKUs or warehouses |
AnyDB simplifies inventory by giving you structure where it matters, and flexibility where it counts.