Order Management & Fulfillment with AnyDB
Overview
This guide shows how to use AnyDB to create and manage customer profiles (whether for individuals or organisations), sales orders, product database, and shipping orders.
Business Problem
When there is no coordination among sales, shipping, and warehousing teams, chaos sets up. Sales orders are managed in spreadsheets, the shipping team delivers the wrong products due to misleading data, lead times increase, and customers become dissatisfied.
Solution Summary
With AnyDB, you can:
- Customise this Order Management & Fulfillment database to suit your operational needs
- Link customers to their respective sales orders and shipping journal statuses
- Track progress on the sales order steps
- Segment sales orders by customer, date, freight, destination, etc.
- Assign tasks and review updates in real time
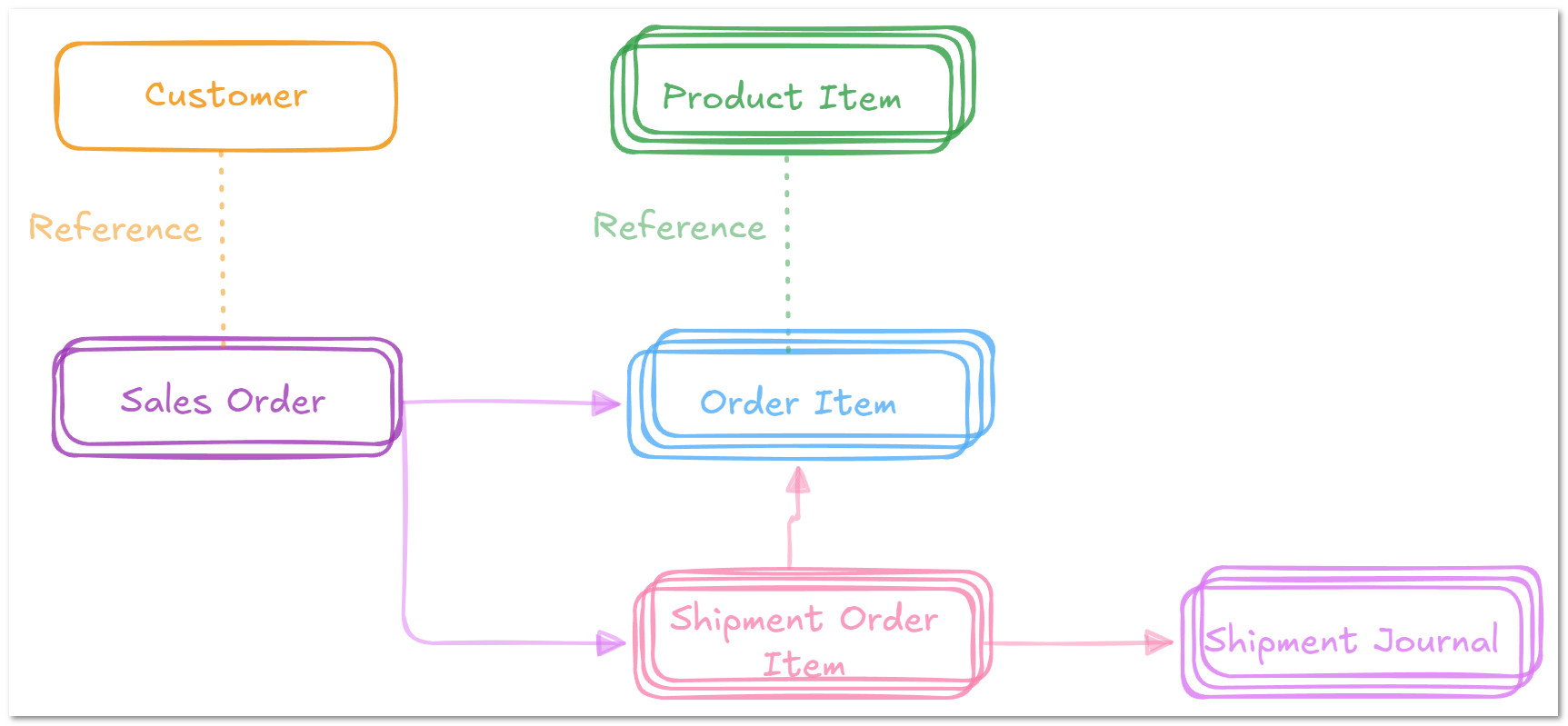
- Definition: A reference is an independent object rather than an attachment.
- Note: Different colours indicate distinct objects.
Step-by-Step Instructions
1. Create a New Database
1.1 Click on + Create new Workspace
1.2 Type a name for the New Workspace and click on Create
1.3 Click on Load Solution
1.4 Select Order Management and Fulfillment on click on Load
- The database includes six primary record types: Customer, Sales Order, Order Item, Product Item, Shipment Order Item and Shipment Journal.
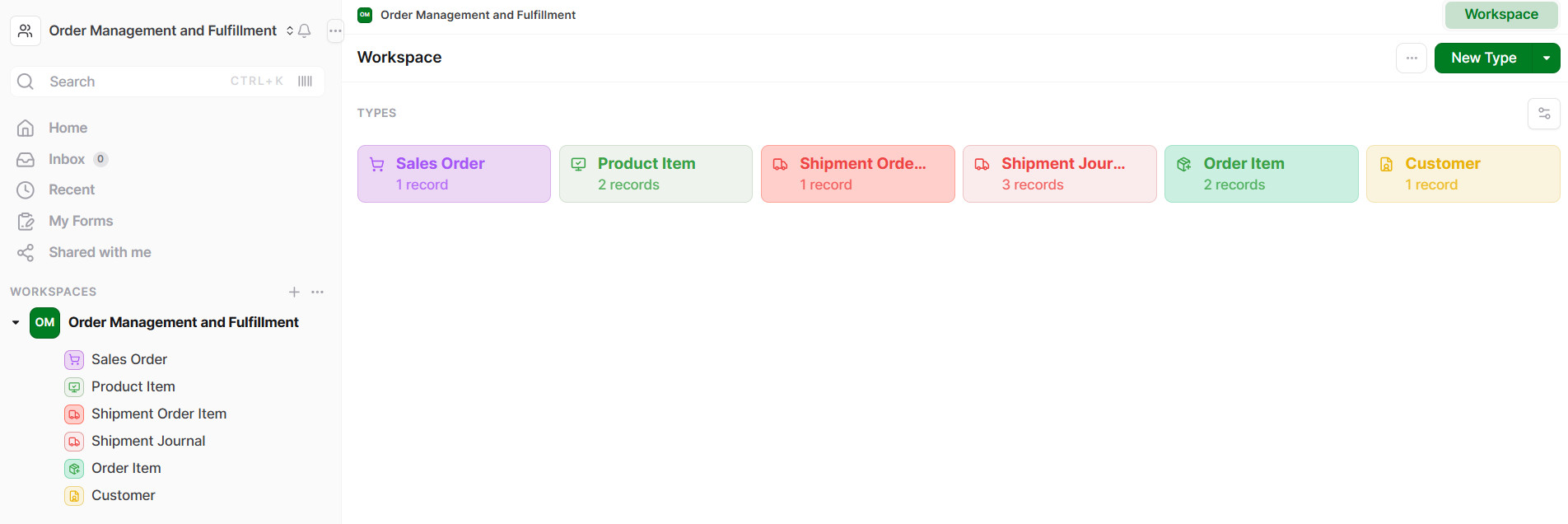
2. Set Up the Customer Profile
2.1 In the Workspace, click on Customer
2.2 Click on New Customer
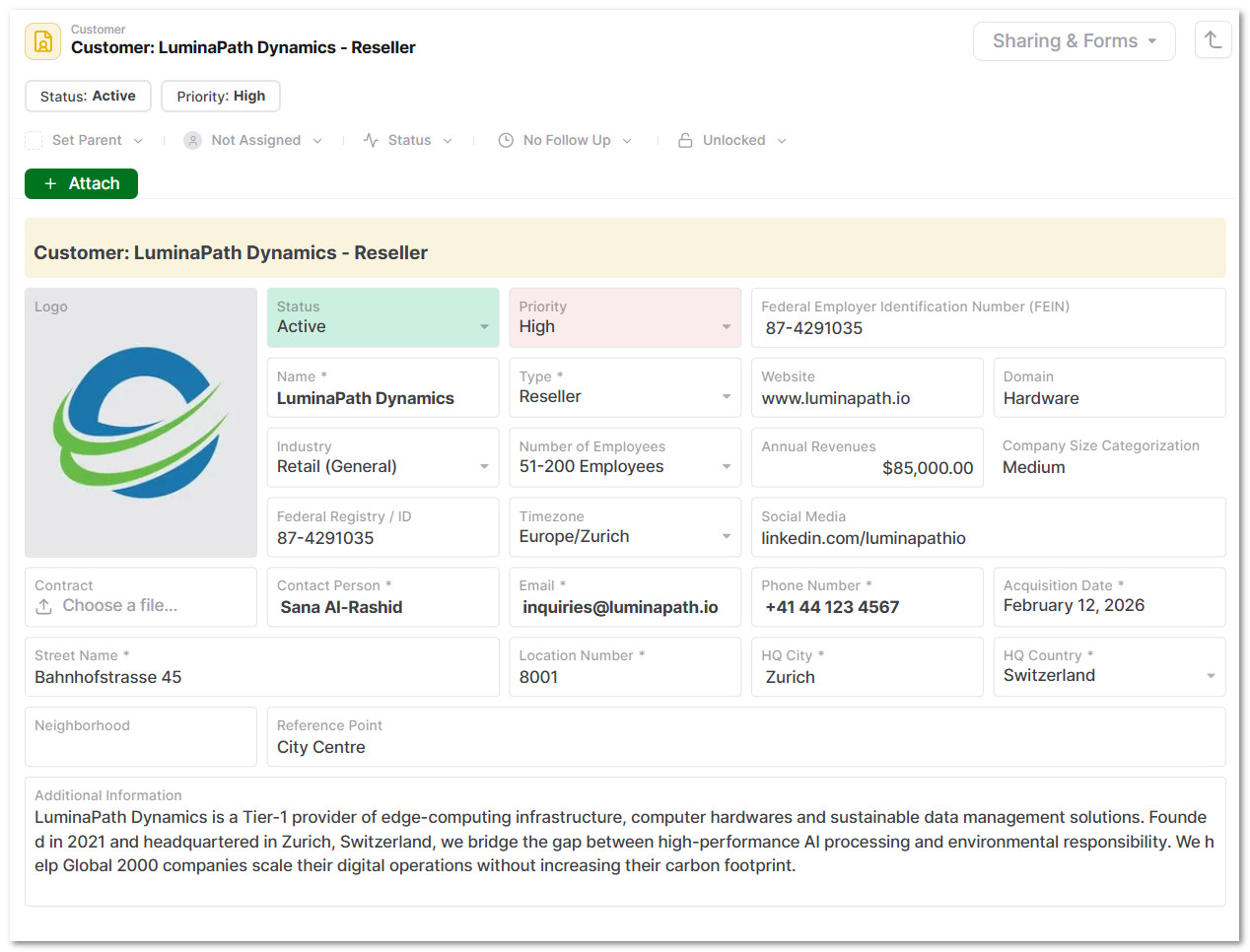
2.3 Fill out all the relevant fields related to the customer
- Key fields include Status, Priority, Name, Logo, Domain, Number of Employees, Tax ID, Address and Website, along with other organisational and contact details.
3. Create a Sales Order
3.1 Return to the Workspace
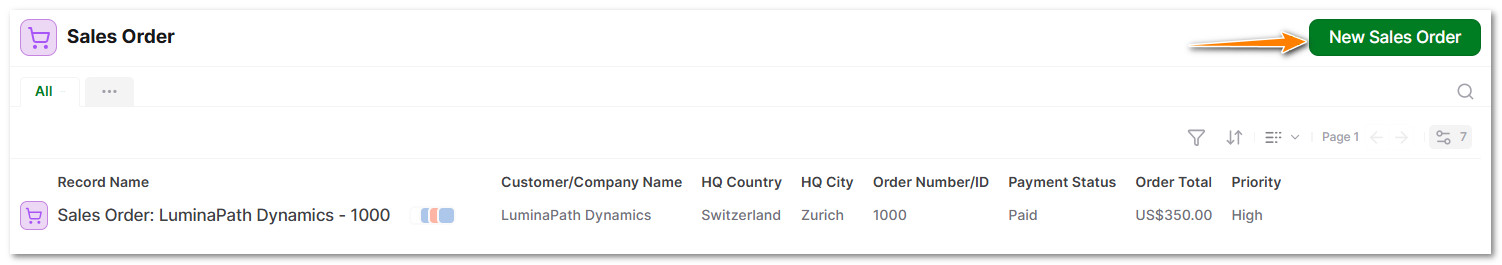
3.2 Click on Sales Order
3.3 Click on New Sales Order
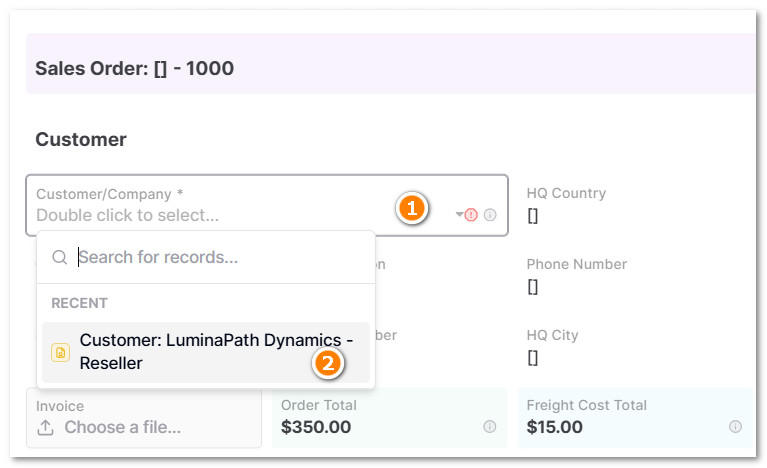
3.4 In Customer Section, Select the respectively Customer Record
- This is a reference cell used to link specific customer data to the sales order automatically.
- A document, such as an invoice and contract, can be attached to the record.
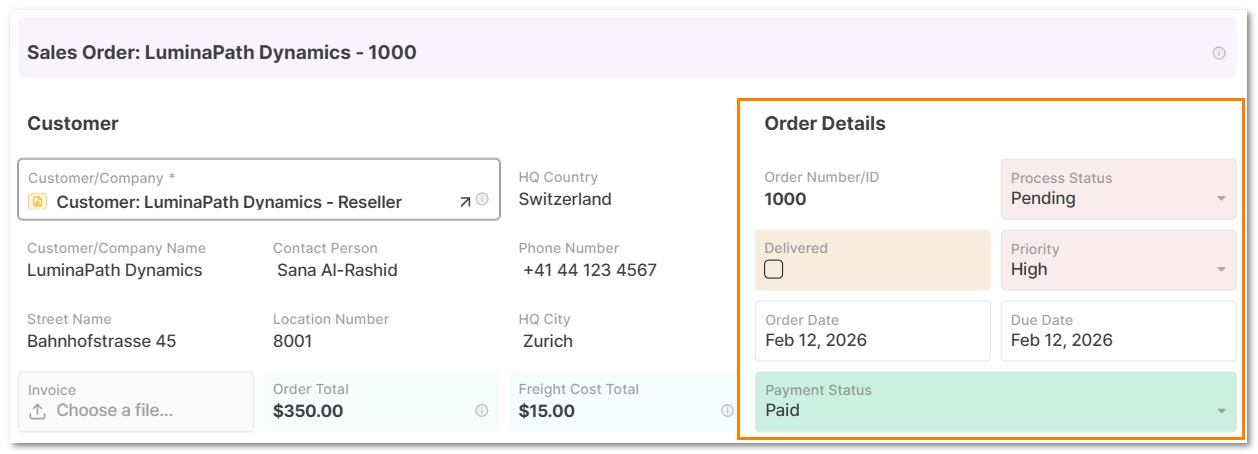
3.5 In Order Details, select the Priority, Order Date and Current Status
4. Add Order Items to the Sales Order
4.1 In the Sales Order Line Items section, click on + Order Item
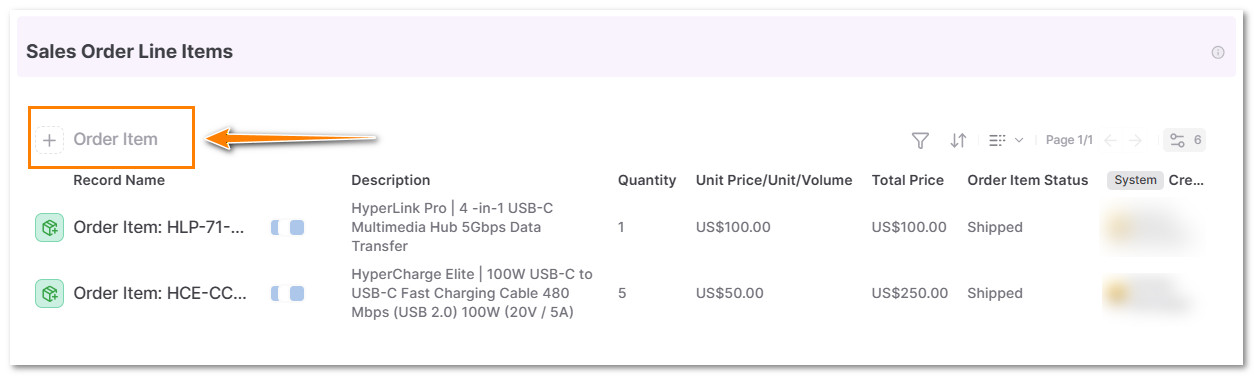
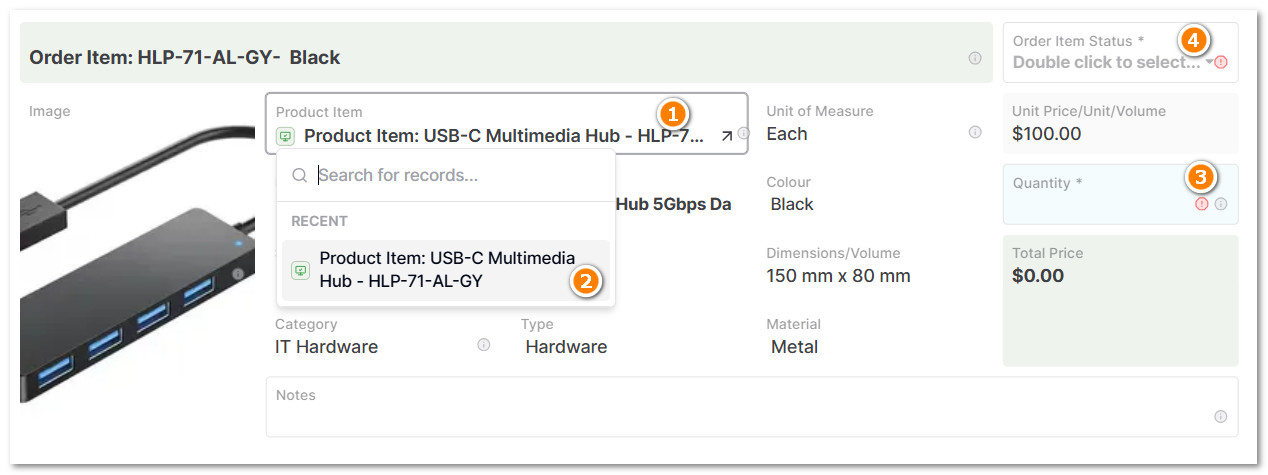
4.2 Click in the Reference Cell and Select the Product Item from the Product Item Database
- Type a quantity and set the current status of the order item.
- The Product Item Database is a set of independent objects (not attachments) that describe each product's characteristics, unit price, SKU, category, dimensions, material, unit of measure, and description.
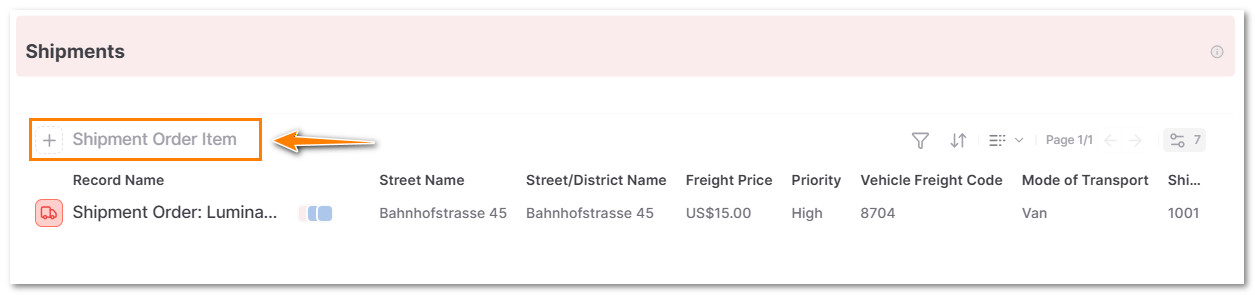
5. Add an Shipment Order Item
5.1 Return to the Sales Order

5.2 In the Shipments section, click on + Shipment Order Item
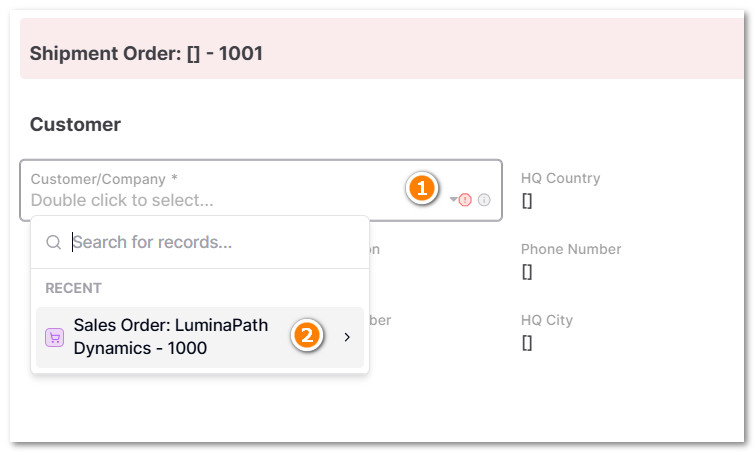
5.3 In Customer Section, Select the respectively Sales Order
- This is a reference cell used to link specific customer data from the current sales order to the shipment order automatically.
5.4 In Shipment Details, select the Priority, Order Date, Mode of Transport, Freight Code and Current Status
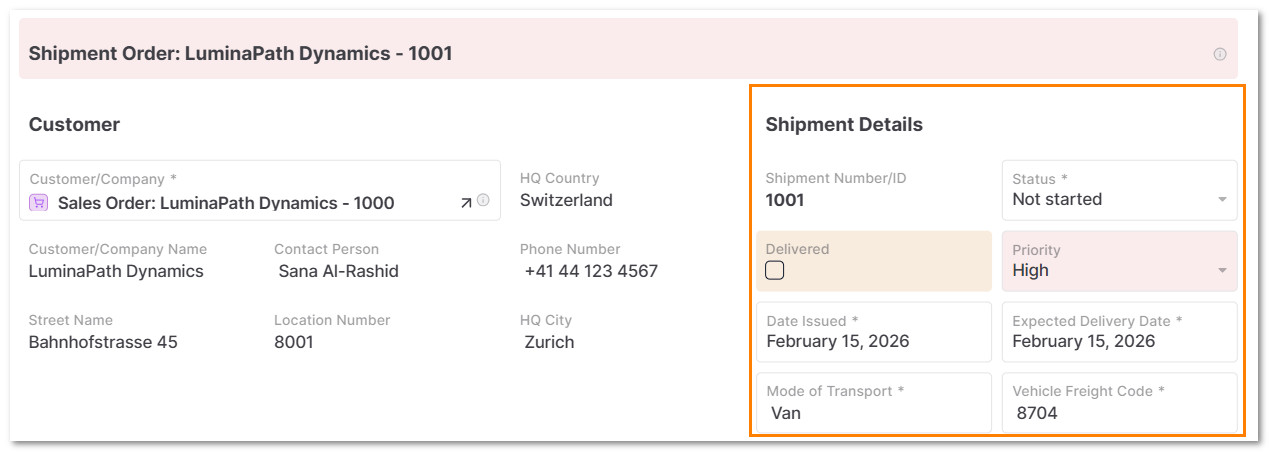
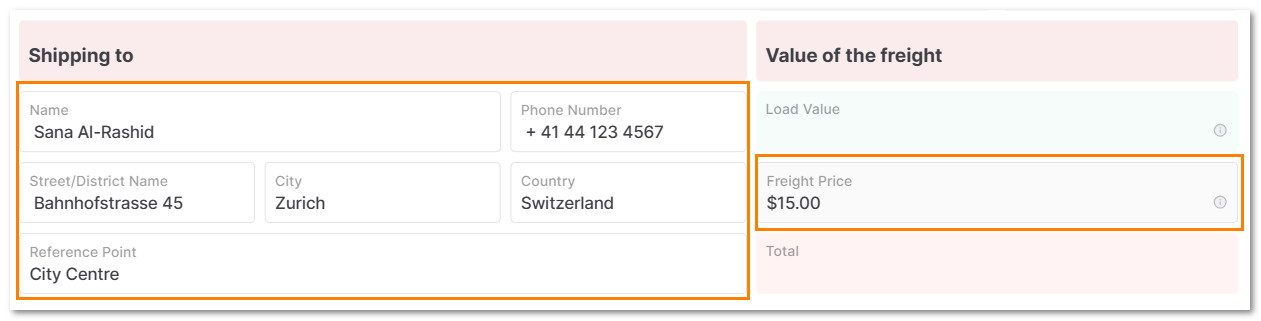
5.5 In Shipping to add the destination details and the price of the freight.
5.6 Click on + Attach and select the same Order Items from the respectively Sales Order.
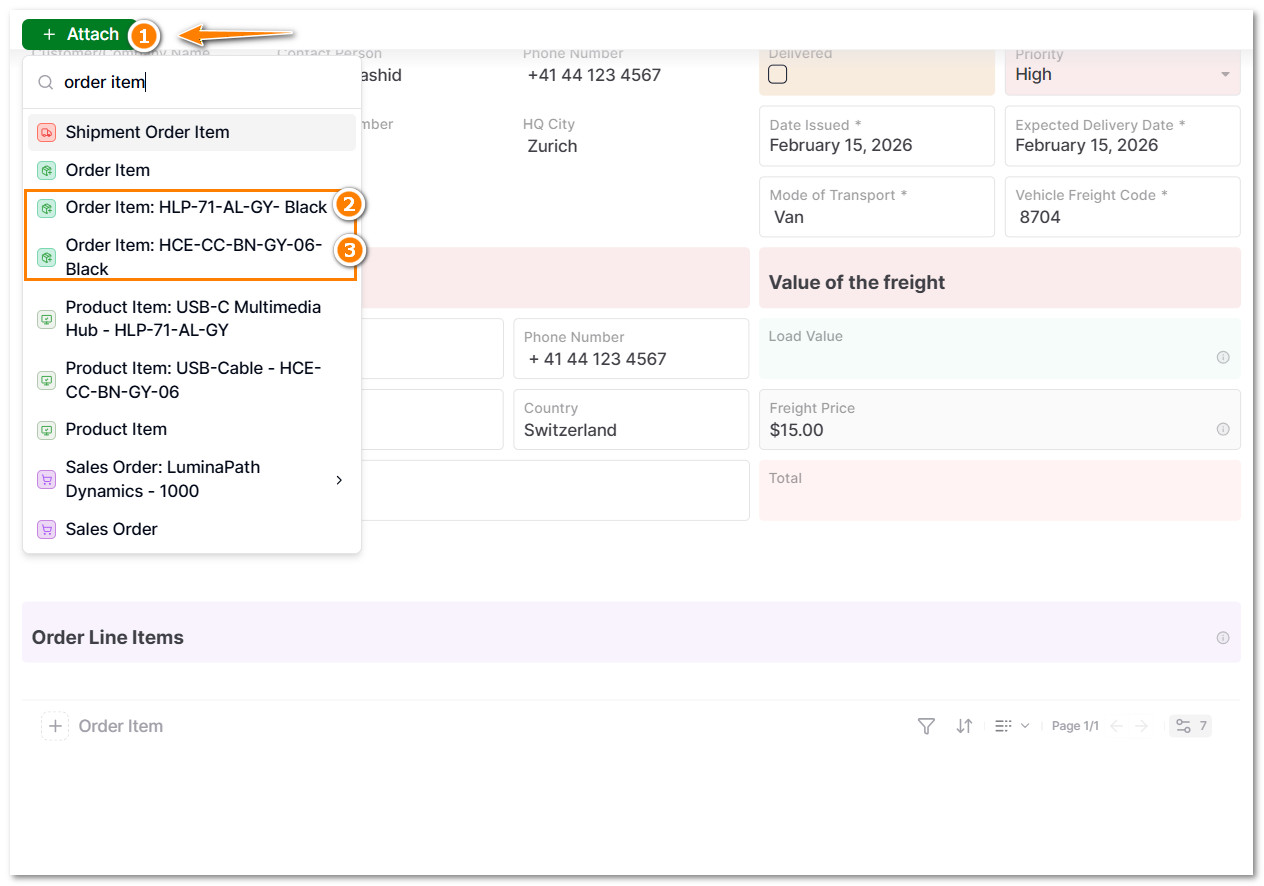
- The shipping lead or team can view all order item details for this particular sales order.
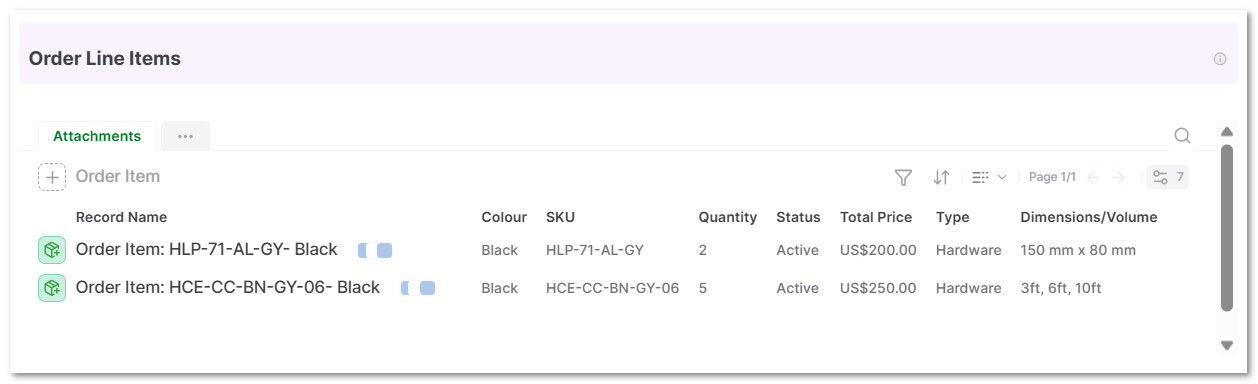
5.7 In the Shipment Journal Section, Click on + Shipment Journal
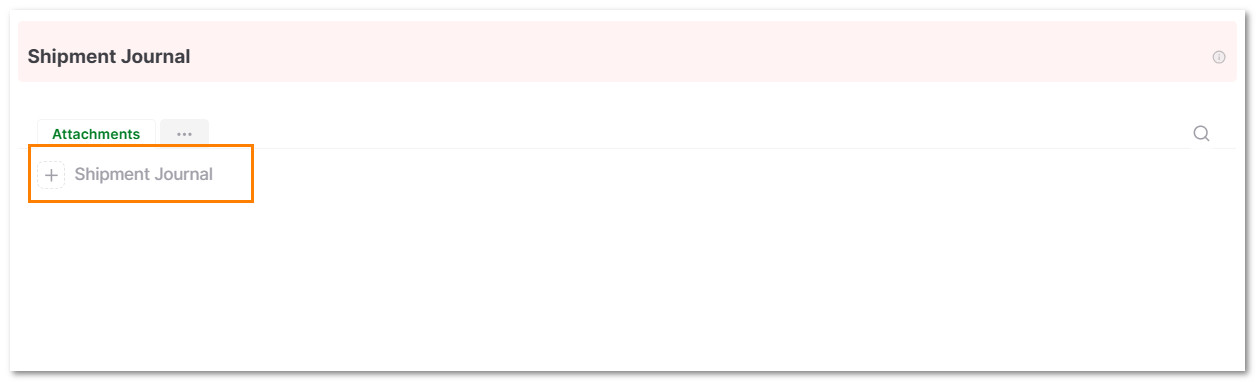
5.8 Select the Date, the current Status such as "In Transportation", or "Delivered", Estimated Delivery Date, Real Delivery Date, add notes and a picture of the current event.
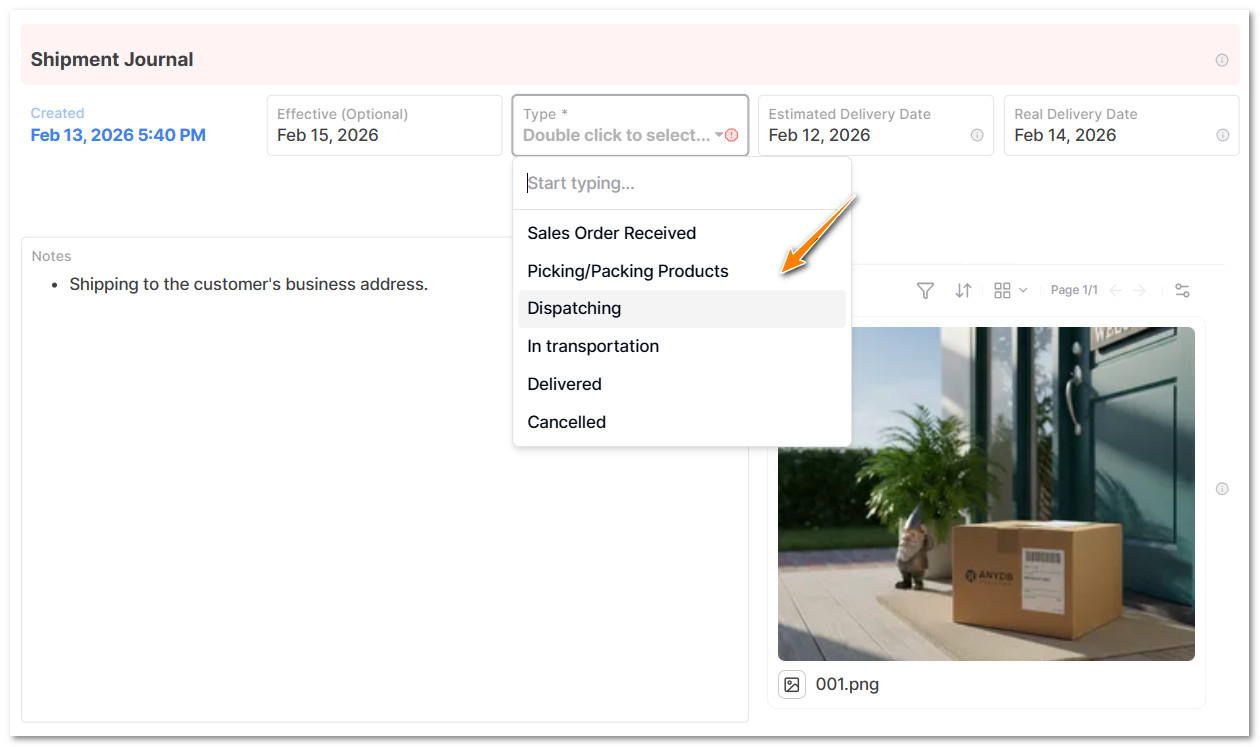
- Returning to the Shipment Order Item, you can view and monitor all shipment events in the Journal Section.
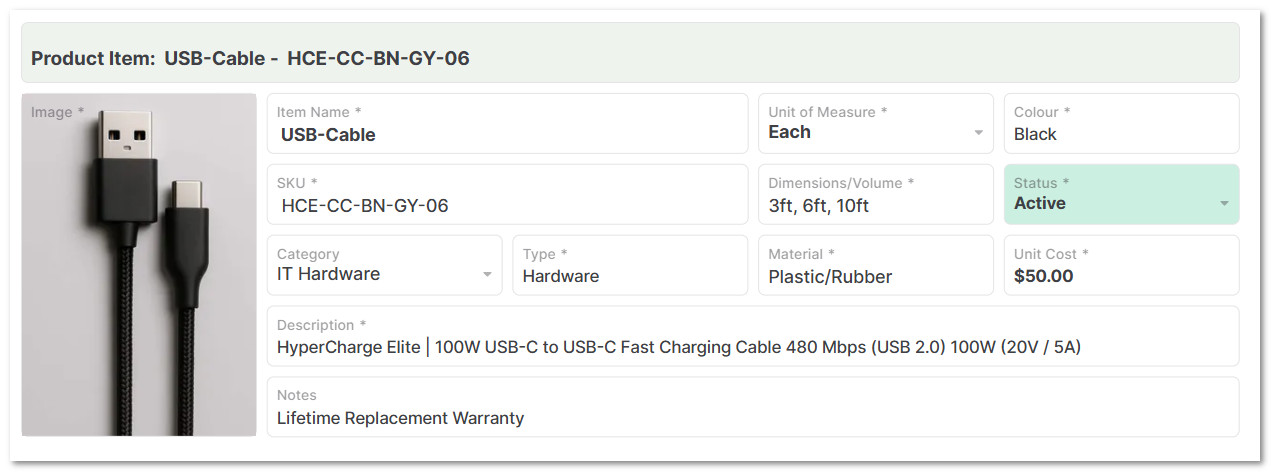
6. Create a Product Item Database
6.1 In the Product Item Record, click on New Product Item
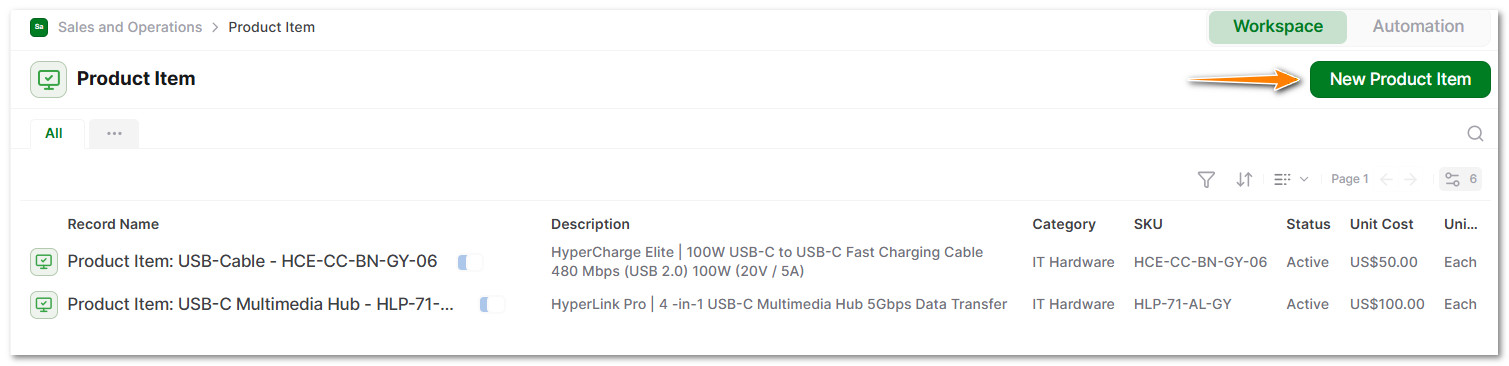
6.2 Add all product details, such as: SKU, description, unit of measure, color, category, volume/dimensions, unit cost, inventory status, product image, and notes.
Data Model & Structure
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Customer | Track and manage a customer profile |
| Sales Order | Trigger the warehouse to pick and pack the goods |
| Order Item | Add a product to the order item |
| Product Item | Add details of a product |
| Shipment Order Item | Dispatch goods to customers |
| Shipment Journal | Signal the events related to the shipment |
Reporting & Views
Use filters and saved views to track:
- Sales Orders and Shipment Order Items by owner, time period, customer, value, status, location, freight, etc.
- Securely share saved views with customers, internal team, and partners.
- Example: Sales Orders from Customer A with third-party company.
Sharing & Collaboration
- Assign records to individuals or teams
- Track progress collaboratively with comment threads
- Use status indicators
- Link updates to weekly reports or team check-ins
- Share views with leadership for transparency
Tips & Best Practices
- Set a follow-up date to avoid missing any steps.
- Update progress regularly, not just at the end.
- Use logistics techniques such as Milk Run and Just-in-Time (JIT) to deliver goods efficiently.
Pro Tip: Integrate the Order Management & Fulfillment database with the Inventory Management database.
Who This is For
- Leadership Teams – for company-wide alignment on strategic priorities
- People Managers – for team-level goal setting and accountability
- Individual Contributors – to connect daily work to higher-level impact
- Chiefs of Staff / Ops – to monitor progress and remove blockers
Why Use AnyDB for Order Management
| Benefit | How AnyDB Supports It |
|---|---|
| Relational "Object" Structure | In AnyDB, an order isn't just a record; it's a connected object. |
| Workflow Automation (No-Code) | You can automate actions without hiring a developer |
| Transparent Progress | Live status, confidence levels, and update history |
| Custom Views | Filters by team, time, or status |
| Review-Ready | Use in weekly or quarterly review cycles |
| Seamless Collaboration | Unlimited Guest Access: external vendors or shipping partners |
AnyDB provides a centralised workspace for collaboration and the flexibility to adapt to operational changes.