Roles
AnyDB Roles are a key part of the platform's fine-grained role-based permissions model, allowing precise and flexible management of user and group permissions across all system resources.
The permission model is designed to give teams detailed control over who can do what—at the level of individual Teams, Databases, Records, Users, and Groups. Permissions are assigned via roles, which can be combined and inherited through group membership, and explicitly restricted where necessary.
This design enables organizations to enforce strict access boundaries while still supporting collaborative workflows and scaling across teams.
Currently, all roles in AnyDB are built-in, but support for custom (user-defined) roles is planned in future releases.
Role-Based Permissions
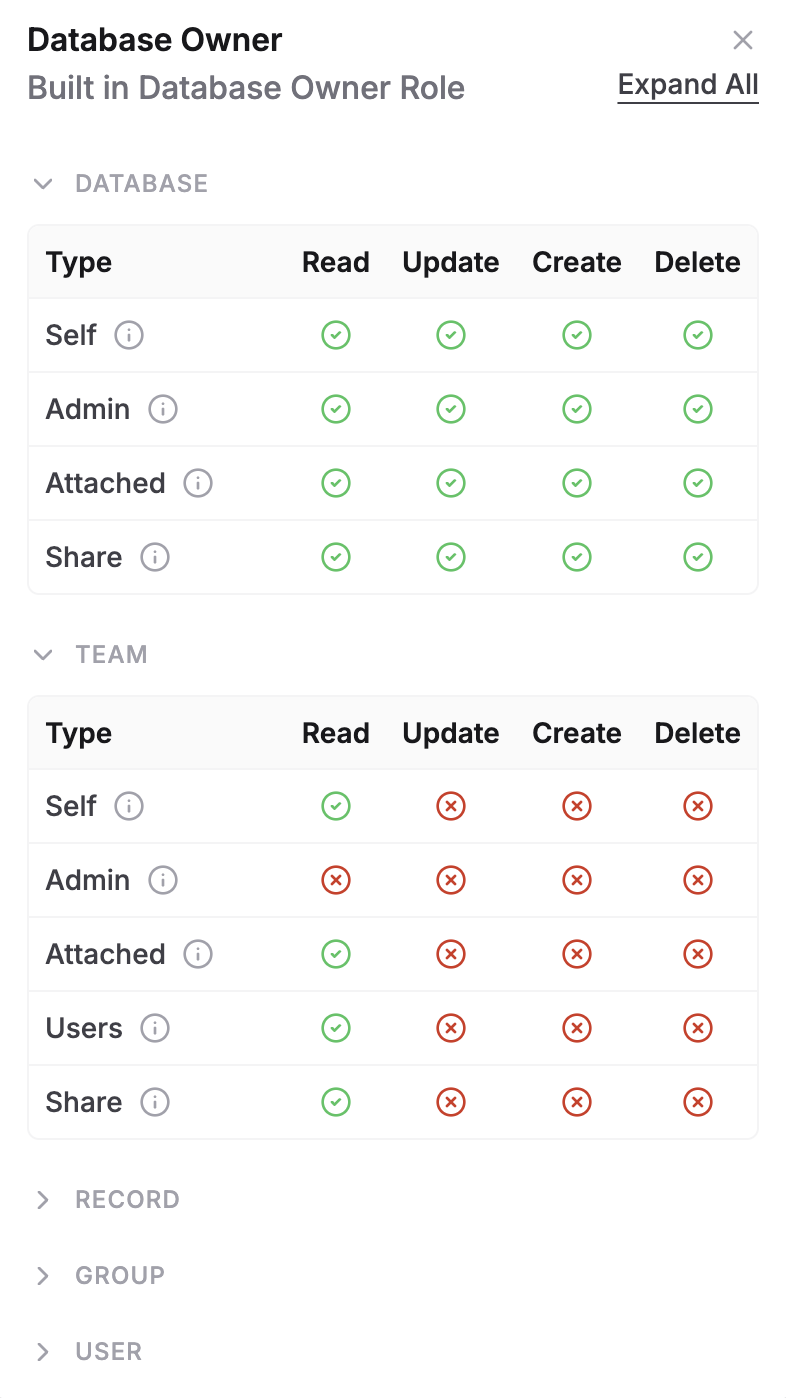
Each role provides one or more of the following permission levels, depending on the resource:
- Read – View access to the resource.
- Write – Ability to modify the resource.
- Create – Ability to add new instances of the resource.
- Delete – Ability to remove the resource.
These permissions are assigned per resource type. For example, a role may grant write access to a Database but only read access to the Team it belongs to.
Assigning Roles
Roles can be assigned to:
- Individual users
- Groups (using AnyDB Groups )
If a user is part of multiple groups or has roles assigned directly, they may inherit multiple sets of permissions. The roles can be assigned to users or group from the Team Properties panel as shown below.
Permission Inheritance and Resolution
AnyDB supports permission inheritance and merging. The effective permissions for a user are computed based on the combination of:
- Roles assigned directly to the user
- Roles inherited through group memberships
Effective Permission Rules
When resolving permissions, the following rules apply:
- Permissions are additive: A user receives the highest level of permission available across all assigned roles (via group or direct assignment).
- Explicit deny takes precedence: If a permission is explicitly denied on a resource, it overrides any other permissions—regardless of role or group.
Example
Consider a user with:
- The Team Member role, which grants:
- Read-only access to Team properties
- No access to Databases
- The Database Member role (via a group), which grants:
- Read and Write access to a specific Database and its Records
Result:
- The user can view Team properties.
- The user can read and write to the Database as permitted by the Database Member role.
However, if an explicit deny is configured for that user or group on the Database resource, access will be blocked, even if roles suggest otherwise.
Viewing Effective Permissions
Users and admins can view effective permissions for each resource directly in the AnyDB UI:
- Team: Navigate to the Team properties and open the Roles panel.
- Database: Go to the Database properties and open the Access panel.
- Record: Click the vertical three-dot menu on the record and select the Permissions panel.
These panels show the resolved (effective) permissions based on all applicable roles, including group inheritance and explicit denies.
Future Enhancements
- Support for user-defined roles, allowing teams to create custom permission sets tailored to their workflows.
Best Practices
To get the most out of AnyDB Roles, follow these recommended practices:
- Use roles consistently: Assign roles at the group level when possible to simplify user management.
- Avoid direct assignments unless necessary